ISSUE1650
- Mark Abramowicz, M.D., President: no disclosure or potential conflict of interest to report
- Jean-Marie Pflomm, Pharm.D., Editor in Chief: no disclosure or potential conflict of interest to report
- Brinda M. Shah, Pharm.D., Consulting Editor: no disclosure or potential conflict of interest to report
- Review the pharmacokinetics of dexlansoprazole and its potency in increasing intragastric pH.
A reader commented that our recent article on Drugs for GERD and Peptic Ulcer Disease did not include enough information on dexlansoprazole (Dexilant, and generics), a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) claimed to provide "all-day and all-night relief from heartburn". Dexlansoprazole recently became available generically, but it is much more expensive than other generic PPIs.
Dexlansoprazole is the R-enantiomer of lansoprazole (Prevacid, and others). Dexilant (and generics) is a delayed-release capsule formulation of dexlansoprazole that releases the drug at two separate times, resulting in two peak serum concentrations (one within 1-2 hours and a second, higher peak within 4-5 hours) and a longer duration of action compared to other PPIs. In a study in healthy volunteers, those who took dexlansoprazole 60 mg once daily had an intragastric pH >4 for a mean of 17 hours on the fifth day of treatment. Taken in the morning, dexlansoprazole will reduce gastric acid secretion into the evening, but not throughout the night.
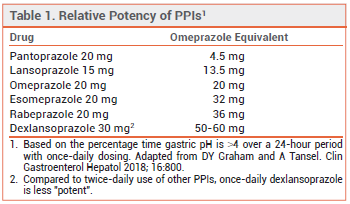
The table in our article that compared the potency of PPIs available in the US did not include dexlansoprazole. It has been updated here and in the online version of the article (see Table 1). Based on its duration of action with once-daily morning dosing, dexlansoprazole appears to be the most potent PPI. In clinical practice, however, other PPIs are often taken twice daily (morning and evening) to prevent nocturnal acid breakthrough. Compared to twice-daily use of other PPIs, once-daily dexlansoprazole is less "potent". For around-the-clock acid suppression, twice-daily dosing of another PPI, such as esomeprazole or rabeprazole, is more likely to be effective.